Types of electricity rates
Customers can now choose Time-of-Use, Tiered, or Ultra-low. For residential and small business customers that buy electricity from their utility, there are three different types of rates (also called prices here). The Ontario Energy Board sets rates once a year on November 1.
With TOU and ULO, the price depends on when you use electricity. This means you can help manage your electricity costs by shifting your usage to lower price periods when possible.
With Tiered, the price depends on how much electricity you use overall in a month.
Current prices
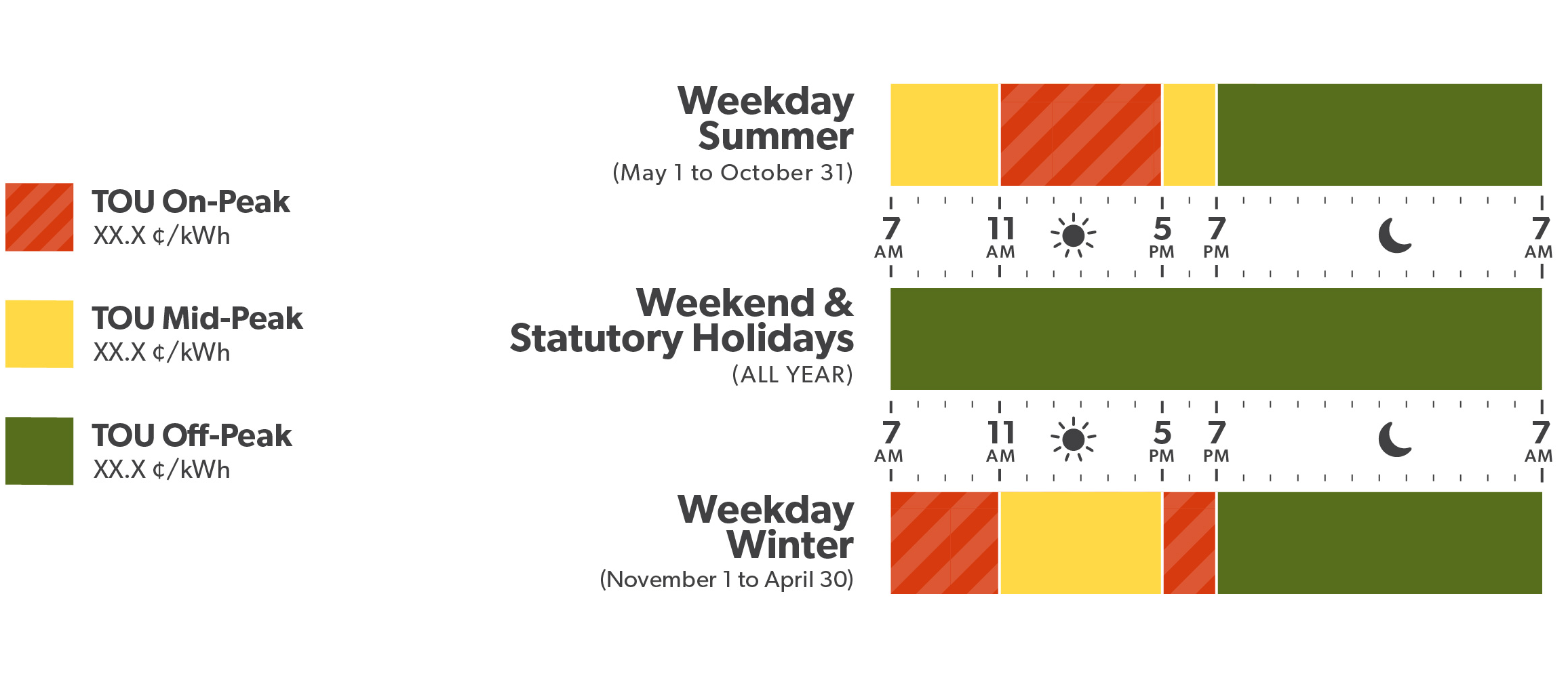
Time-of-Use (TOU)
| TOU Price Periods | TOU Prices (¢/kWh) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Off-Peak | Weekdays 7 p.m. – 7 a.m. Weekends and holidays all day |
Weekdays 7 p.m. – 7 a.m. Weekends and holidays all day |
7.6 |
| Mid-Peak | Weekdays 11 a.m. – 5 p.m. | Weekdays 7 a.m. – 11 a.m. and 5 p.m. – 7 p.m. | 12.2 |
| On-Peak | Weekdays 7 a.m. – 11 a.m. and 5 p.m. – 7 p.m. | Weekdays 11 a.m. – 5 p.m. | 15.8 |
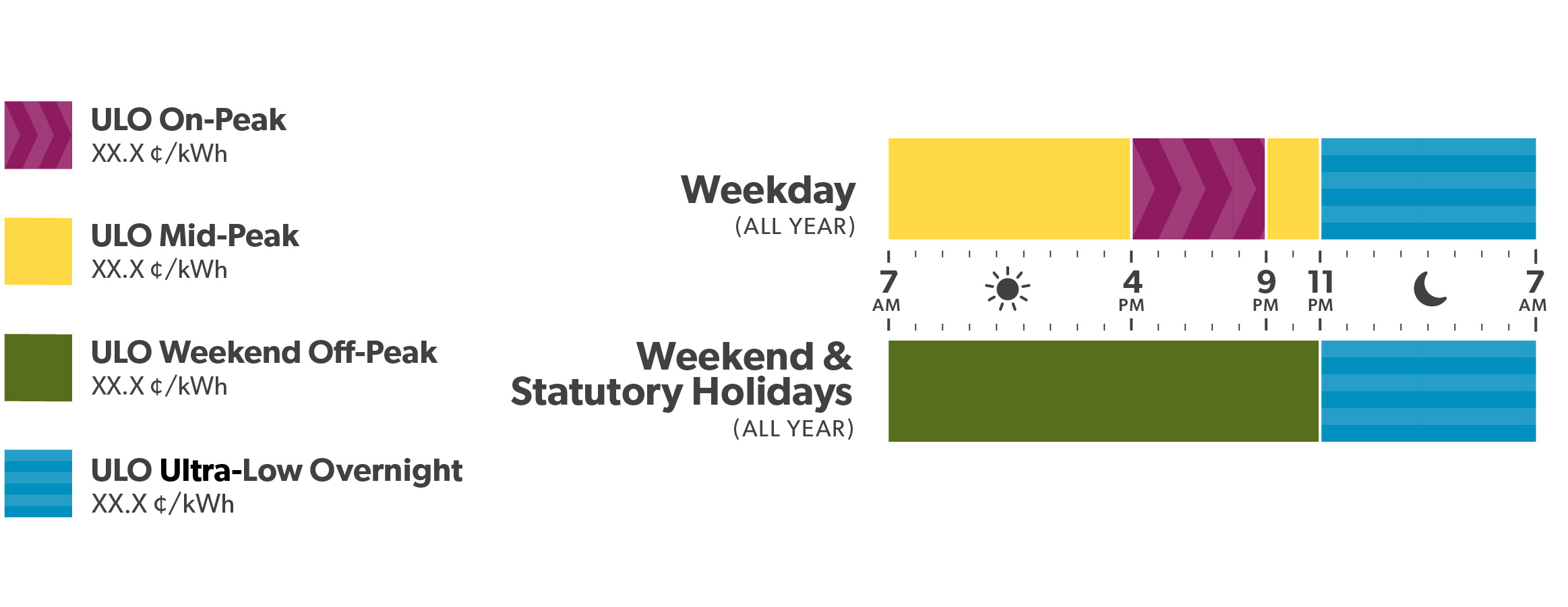
Ultra-Low Overnight (ULO)
| ULO Price Periods | All Year | ULO Prices (¢/kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Low Overnight | Every day 11 p.m. – 7 a.m. | 2.8 |
| Weekend Off-Peak | Weekends and holidays 7 a.m. – 11 p.m. | 7.6 |
| Mid-Peak | Weekdays 7 a.m. – 4 p.m. and 9 p.m. to 11 p.m. | 12.2 |
| On-Peak | Weekdays 4 p.m. – 9 p.m. | 28.4 |
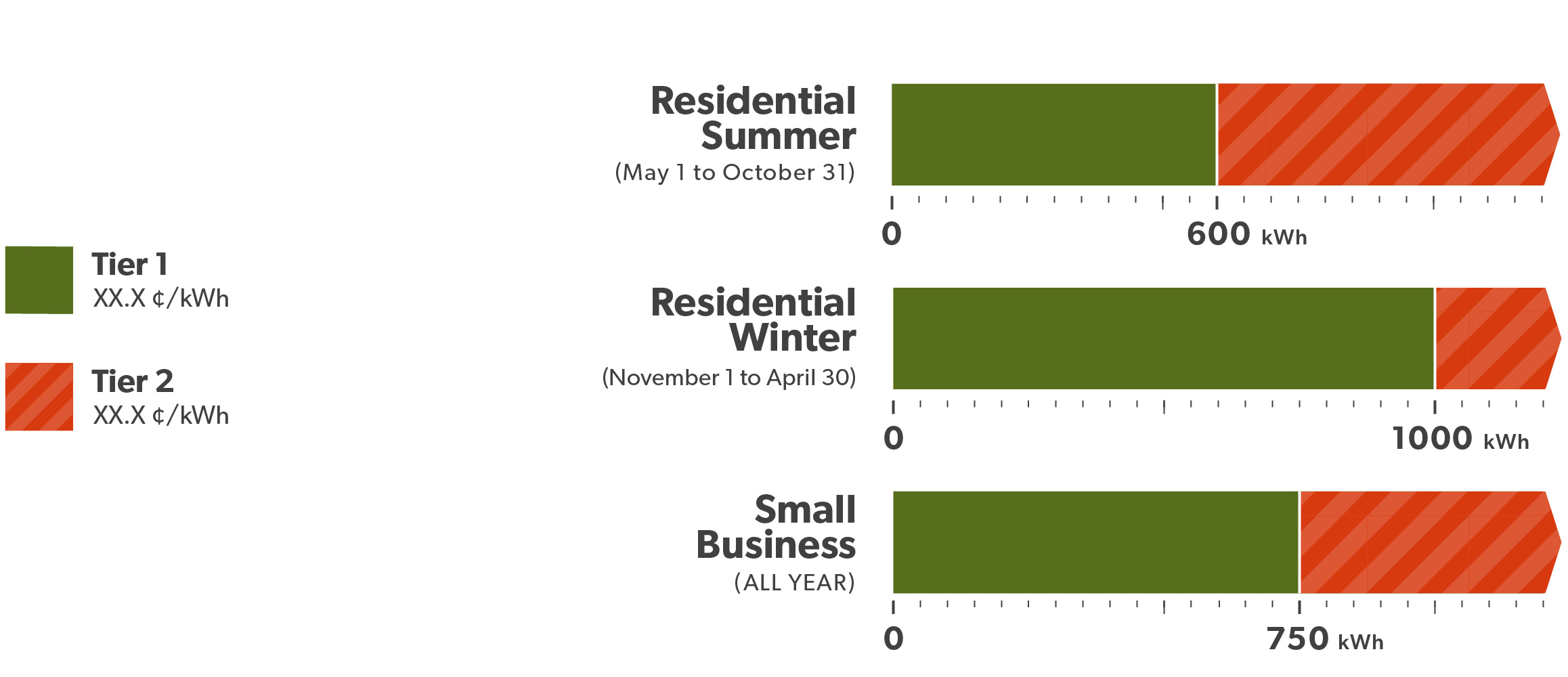
Tiered
| Tier Thresholds | Tiered Prices (¢/kWh) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | Residential – first 1,000 kWh/month
Non-residential – first 750 kWh/month |
Residential – first 600 kWh/month
Non-residential – first 750 kWh/month |
9.3 |
| Tier 2 | Residential – for electricity used above 1,000 kWh/month
Non-residential – for electricity used above 750 kWh/month |
Residential – for electricity used above 600 kWh/month
Non-residential – for electricity used above 750 kWh/month |
11.0 |
Considering a switch? Try out the virtual calculator to see what plan may work best for you.

Power is personal. Some customers may prefer TOU prices. For instance, customers who work different shifts may be able to use more of their electricity at times when lower off-peak prices apply, and customers who recharge their electric cars may also want to take advantage of the lower off-peak prices that apply at night. Others may favour Tiered prices because they want the flexibility to do their household chores at any time of the day, or their total usage rarely exceeds 600 kWh in a month in summer, or 1,000 kWh in a month in winter.
Whatever you choose, one thing remains certain: the less electricity you use, the less you pay. And no matter what your price plan is, you are eligible for government programs like the Ontario Electricity Rebate and the Ontario Electricity Support Program.
Are you thinking about opting out of TOU prices in favour of Tiered prices? Here are a few things to consider. Make sure you have some of your recent electricity bills handy as you go through the information below. Keep in mind the effect of COVID-19 on your electricity use (for instance, you may be working from home when you normally wouldn’t be). Most of the information you will need is on the Electricity line of your bill.

Electricity Charges
How much of your bill does Lakeland keep?
As a utility, Lakeland collects 100% of the charges on the bill, but we only keep a small portion of those charges. The rest is passed on to the government.